Your one-stop guide to trading cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency market is beginning to attract retail and institutional investors. With more than 10,000 cryptocurrencies available in early 2021, traders have plenty of opportunities to speculate on these highly-volatile assets. We’ve covered everything you need to learn how to trade cryptocurrencies with CFDs.
Get started- Learn to trade
- popular markets guide
- cryptocurrency trading guide
What is cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a decentralised digital currency. It works through a system of peer-to-peer (P2P) transaction checks, with no central server. All the transactions are added to a shared digital ledger called blockchain through a process that is known as mining.
Cryptocurrencies differ from currencies such as pounds sterling or dollars, which are known as fiat currencies. A fiat currency is issued by a government and guaranteed and controlled by a central bank. This means a fiat currency can be more stable, but it can also be manipulated by a government – for example, if a decision is taken to print more money. Both fiat and cryptocurrencies fluctuate due to market conditions but Fiat currencies are also subject to government-led price fluctuations.
.jpg)
Decentralised
Cryptocurrencies have no central authority, making them unlike fiat currencies, which are controlled by central authorities and banks. Instead, cryptocurrency transactions are processed and validated by an open and distributed network.
Immutable and irreversible
Cryptocurrency’s immutability is based on several principles: it should be impossible for anyone but the holder of a private key to move crypto assets; all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, which makes it impossible to hide or change any transaction.
Anonymous
Usually there is no need for cryptocurrency holders to identify themselves, when making transactions. Users can use their digital identities and digital wallets to use the decentralised system and authenticate their transactions securely. Still, you should note that wallet addresses are not completely anonymous — they are pseudonymous, which means they act as a placeholder for the wallet owner’s identity. However, there are cryptocurrencies, which have increased levels of anonymity, for example, the main two privacy coins Zcash (ZEC) and Monero (XMR).
Scarcity or limited supply
Fiat currencies have an unlimited supply, which enables central banks to manipulate the value of currencies according to their policies. Many cryptocurrencies, in turn, have a limited and pre-defined supply, coded into the underlying algorithm, which makes them deflationary in nature. Although some of the most popular cryptocurrencies have fixed maximum supply, like bitcoin (BTC), others, like Ethereum’ ether coin (ETH), have a constant flow of new assets added to their ecosystem. Still, the developers add a fixed amount of ether per year.
What is cryptocurrency used for? It is a digital asset conceived for use as a medium of exchange. Cryptocurrencies run on a blockchain that uses cryptography to secure transactions, control the supply of additional units and corroborate transfers.
Blockchains are digital databases that store cryptocurrency transactions in blocks requiring complex mathematical calculations to record and verify. Cryptocurrencies are stored in electronic wallets, which are highly secure, as they use a unique private key to verify the owner of the currency.
Cryptocurrencies have become popular among traders and an asset class in their own right. Their volatile nature provides ample opportunities for traders but also makes investment in cryptos riskier.
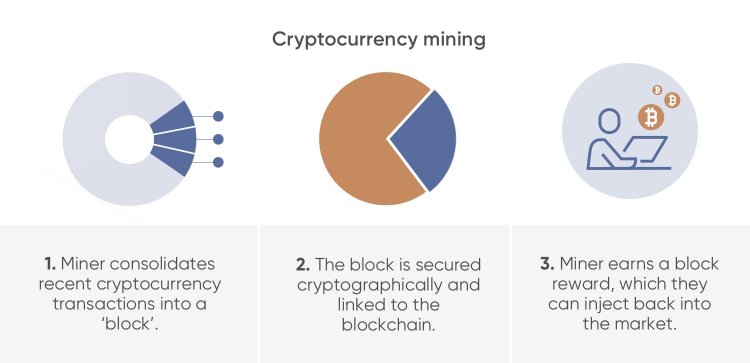
What is cryptocurrency mining?
In the cryptocurrency world, mining is a process by which new coins, for example bitcoins (BTC), enter circulation. It is also a key component of the development and maintenance of the blockchain ledger.
Cryptocurrency mining ensures that recent transactions are checked and new blocks are added to the blockchain.
-
Transactions checking. Mining computers choose pending transactions from a pool and ensure the sender has enough funds to complete the transaction.
-
New block creation. Mining computers compile valid transactions into a new block and try to produce the cryptographic link to it by solving a complicated algorithm. When the computer creates the link, it adds the block to the blockchain file and shares the update across the network.
The history of bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency
Where does cryptocurrency come from? Cryptocurrency history started in 2009 with the launch of bitcoin. The first decentralised cryptocurrency, bitcoin (BTC) was created by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, and it has since paved the way for many other alternative cryptocurrencies, known as “altcoins”.
Although the cryptocurrency was first launched in 2009, it was not until 17 March 2010 that Bitcoin trading became possible, when the first exchange started operating on the now-defunct BitcoinMarket.com.
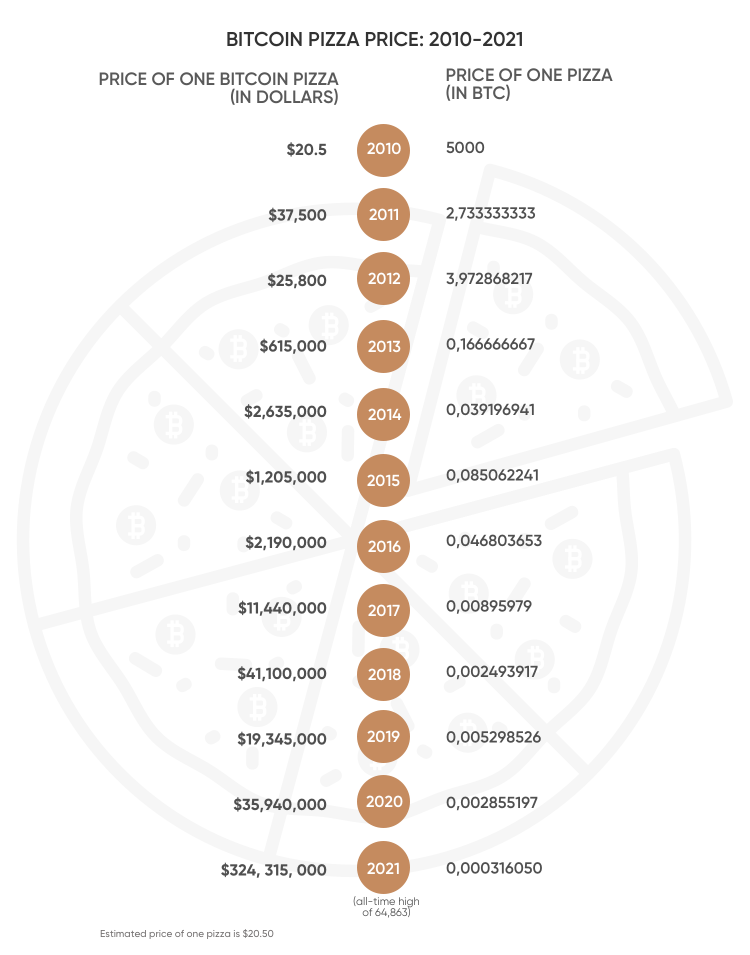
In May 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz made the first real-world transaction by buying two pizzas in Jacksonville, Florida for 10,000 BTC. At that time one bitcoin was worth around $0.0041, which means Hanyecz’ 10,000 BTC for two pizzas cost him $41. It made the estimated price of one pizza $20.50 back in 2010. Let’s see how much that pizza (5,000BTC) would cost in USD in 2021.
This is just for illustration: the value of pizzas, like bitcoin, can go down as well as up.
Bitcoin trading has become controversial thanks to its wild price swings and an exuberance around its rallies that has seen a few investors risk their savings and take out loans to speculate on its value rising. With each spike and retreat in value, it generates dramatic news headlines and attracts even more investors.
-
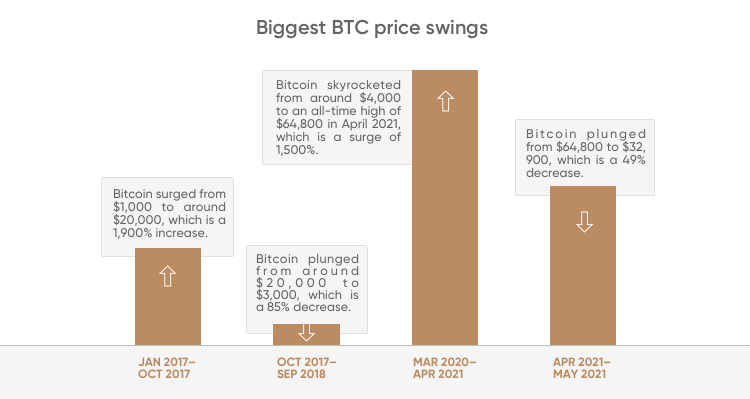
In 2017, the Bitcoin price surged by more than 220% and reached almost $20,000. In 2018, Bitcoin slid sharply down during the “Crypto Winter” of 2018, when it lost more than 60%, sinking to a $3,000 level.
-
In 2021, Bitcoin’s value skyrocketed to its all-time high of $64,863. The growing bitcoin adoption by institutional investors, including Tesla, Square, MicroStrategy and PayPal, contributed to the bullish bitcoin price forecast for the end of this year and beyond. However, the price fell soon after when Tesla’s Elon Musk announced he would no longer accept bitcoin for car purchases. This shows how difficult it is to forecast any cryptocurrency’s price.
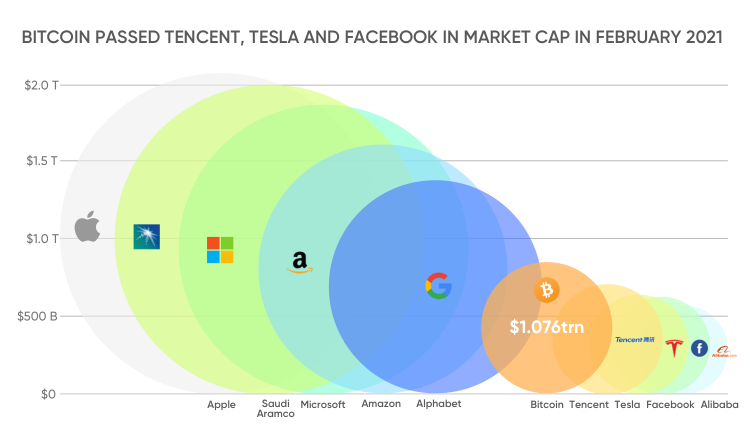
Bitcoin was created with a maximum supply capped at 21 million coins. By May 2021, there were 18.7 million BTC in circulation, representing 89.04% of the maximum supply. One factor is that finite supply has possibly been driving up the price, as an increasing number of bitcoin investors look to secure a limited number of coins. Bitcoin hit a market capitalisation of more than $1trn in February 2021.
The success of bitcoin to date has prompted software developers to launch alternative cryptocurrencies that look to improve on bitcoin’s weaknesses such as its energy-intensive mining and high usage costs, reduce transaction fees and create competition. In early 2021 there were more than 4,000 cryptocurrencies in circulation, although bitcoin remains the most popular, with the largest market value.
Bitcoin halving explained
What is halving? Cryptocurrency halving occurs when the reward for mining new coins is halved. There may be only 21 million bitcoins mined in aggregate. So the reward for bitcoin mining is halved every 210,000 blocks. At the very start, miners earned 50 bitcoins per block mined, four years later miners’ reward was halved to 25 bitcoins. After the second halving they got 12.5 bitcoin for one block.
Today, after the latest block halving in May 2020, miners' reward comprises 6.25 BTC. Therefore, the number of new bitcoins entering the market decreased. The demand for bitcoin is currently forecast to increase, but the supply can’t surge to meet that demand. When the demand exceeds supply, the value of bitcoin usually increases.
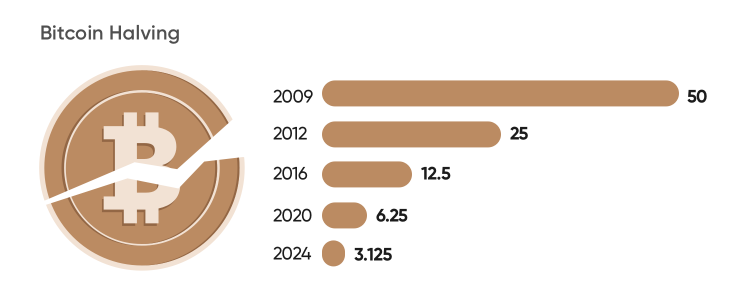
Some bitcoin analysts share a view that bitcoin halving directly influences its price. For example, the first bitcoin halving occurred in 2012. One year later, bitcoin climbed to its peak at the time.
During the second halving in July 2016, bitcoin’s price was fluctuating at around $640. Seventeen months later bitcoin surged to a high of $20,000. According to a popular Stock-to-Flow (S2F) bitcoin prediction model, if the pattern repeats, bitcoin can reach from $100,000 to $288,000 by December 2021. However, past performance is no guarantee of future results.
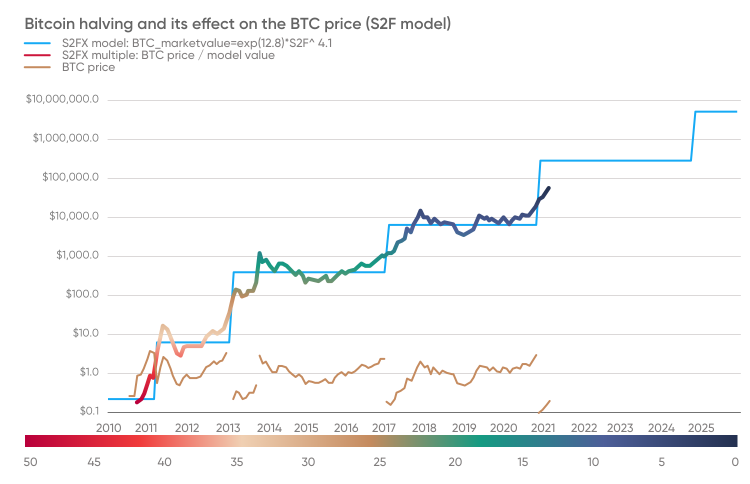
The majority of bitcoins mined every day are sold by miners directly, as they try to cover the energy costs. After the reward is halved, bitcoin offering decreases, which may positively influence the BTC price.
When will bitcoin halve next time? Bitcoin halving occurs approximately once every four years and is watched by millions of bitcoin investors. The next bitcoin halving will be scheduled for 2024. The last of the 21 million bitcoins is estimated to be released in 2140. It means that we have more than 100 years of bitcoin mining ahead.
How many cryptocurrencies are there?
According to CoinMarketCap as of 2 June 2021, there are more than 10,000 cryptocurrencies worldwide. However, not all crypto projects have significant fundamental value. It is believed that the top 20 cryptocurrencies comprise almost 90% of the total cryptocurrency market value.
All cryptocurrency projects should be researched heavily before trading. Many people consider the value of altcoins to be derived from the projects behind the cryptocurrency.
Types of cryptocurrency
All the cryptocurrencies usually fall into three major categories: bitcoin, altcoins and tokens.
-
Bitcoin (BTC) the world’s first and leading cryptocurrency by market cap. Bitcoin is a global peer-to-peer digital payment system that allows parties to transact directly with each other with no need for an intermediary such as a bank. Bitcoin is often talked of as the digital alternative to fiat currencies and gold but regulators argue it is significantly riskier and cannot be compared.
-
Altcoins are defined as cryptocurrencies that are alternatives to bitcoins. Altcoins can differ from bitcoin in a variety of ways. Some may have a different economic model and others may use different underlying algorithms or blocksize. Altcoins encompass a wide range of different uses. For example, Ethereum (ETH), the world’s first programmable blockchain, enables developers to build and deploy decentralised applications (dApps) and smart contracts. IOTA (MIOTA) is specifically designed to be a new data transfer and transaction settlement layer for the machine economy and the Internet of Things (IoT). At the end of May 2021, the top five altcoins by market cap were: Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT), Binance Coin (BNB), Cardano (ADA), Ripple (XRP).
-
Tokens, unlike bitcoin and altcoins, do not operate independently and rely on the network or another cryptocurrency. They don’t have their own blockchain, but instead, are built on top of an existing cryptocurrency’s blockchain. The ethereum platform has by far the most tokens deployed on it, including Chainlink (LINK) and Basic Attention Token (BAT). NEO is often referred to as the Chinese rival to ethereum and a platform for dApps and smart contracts. It also hosts many tokens, including Gas (GAS) and Nash Exchange (NEX).
Cryptocurrency categories
Besides the major types of cryptocurrencies, there are various subtypes that you will likely come across in the crypto world. Here are four terms commonly used to categorise cryptocurrencies that have specific characteristics:
All the cryptocurrencies usually fall into three major categories: bitcoin, altcoins and tokens.
-
Privacy coins - cryptocurrencies that focus on providing private transactions, such as Monero, Zcash, and Dash.
-
Stablecoins - cryptocurrencies that are pegged to ‘stable’ assets such as fiat currencies to reduce price volatility dramatically. Prime examples include Tether, Dai, USD Coin, and Paxos.
-
Exchange tokens - cryptocurrencies created by crypto exchanges to be used primarily on their own trading platform and services. Prime examples include Binance Coin, Huobi Token, and KuCoin.
-
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) - cryptocurrencies that are created or backed by a central bank. The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) is currently developing its digital yuan. The Bank of England suggested it might promote a digital pound it cheekily called Britcoin.
What are the most popular cryptocurrencies?
Investors often wonder which cryptocurrencies to buy. Although there is no definite answer to this question, we can take a closer look at the list of most-traded cryptocurrencies at equitypinnacle.com and compare it with the list of the most valuable cryptocurrencies by market capitalisation from CoinMarketcap.
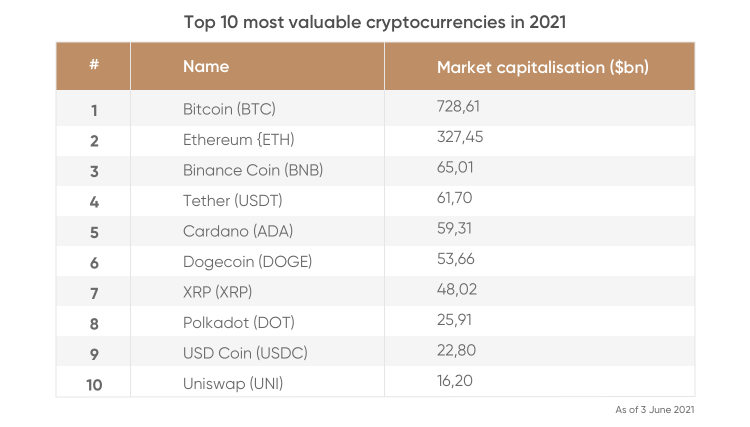
Although both lists are changing every day, driven by the volatile nature of the cryptocurrency market,the long-standing leaders in both ratings aside from bitcoin (BTC) are:
-
Ethereum (ETH): an open platform that enables developers to build and deploy decentralised applications (dApps). The easiest way to think of ethereum is as a programmable bitcoin. Ethereum allows participants to run decentralised blockchain applications called smart contracts. Smart contracts are highly secure, and run with the perfect digital history, making them auditable, trustless and unstoppable. These smart contracts can be programmed without any chance of downtime, censorship or fraud. Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalisation.
-
Ripple (XRP): a real-time settlement system and currency exchange network created by Ripple Labs that uses their native cryptocurrency, XRP, to process transactions. Ripple was designed primarily as a faster payment system. Ripple is considered a speedy, less expensive and more scalable alternative to other digital assets and existing monetary payment systems like SWIFT.
-
Cardano (ADA) is one of the biggest proof-of-stake blockchains, an alternative to ethereum. Both platforms are used for running dApps and smart-contracts and aim to build a connected and decentralised ecosystem. Cardano positions itself as the next generation network over ethereum’s second-generation platform. Cardano’s ADA token is created to ensure holders can take part in the network’s operation.
Trading cryptocurrency vs trading stocks
Crypto vs stocks, what’s the difference when investing and trading?
The history of stock exchanges dates back more than 400 years, and today we know them as primary marketplaces for buying or selling company stocks. Cryptocurrency trading has sprung up over the past decade, which makes it a relatively new part of the global financial marketplace.
Trading cryptocurrency or stocks present many trading opportunities and can be a valuable part of a diversified investment portfolio. However, regulators believe cryptocurrencies come with much higher risks.
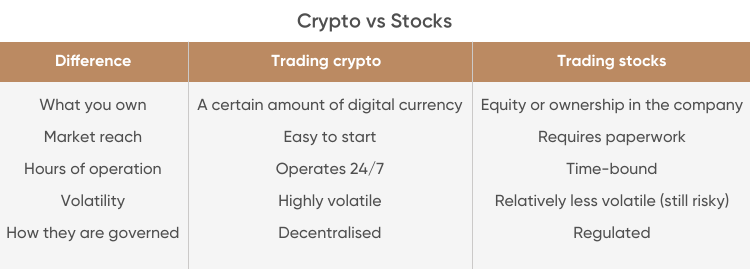
What you own
By buying stocks you become a part owner of a particular company. When you acquire cryptocurrency – be it tokens or coins – you just own a certain amount of the digital currency and don’t necessarily get partial ownership of the company which issued it.
Market reach
The stock market is very mature and requires extensive regulation. It means that you’ll need to do some paperwork to start trading on a traditional stock exchange. In the meantime, it is often easier and less time-consuming to start trading on a crypto exchange.
Volatility
Both markets tend to go up and down in value, so trading is always risky. However, the cryptocurrency market is known for drastic price swings, which can happen overnight, significantly increasing investment risk. Stocks movement, on the other hand, is generally driven by the company’s fundamental performance, so the company’s regular earnings updates can help investors to make informed decisions.
How they are governed
Financial regulators, including the US Securities and Exchanges Commission (SEC) and the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), govern the stock market in their respective jurisdictions. In contrast, there is no central authority regulating the cryptocurrency market. In many crypto projects, governance is distributed among those involved in maintaining and growing its technology.
Why is cryptocurrency so volatile?
Volatility in financial markets refers to fluctuations in an asset’s price. Volatility is an underlying feature of any market’s activity. It can be healthy, with reasonable increases or decreases in price, or extreme, with drastic price swings in either direction.
Volatility provides traders with good opportunities for profits. However, extreme volatility, with sudden spikes in price, can increase the risk and size of losses
Why are cryptos so volatile? Bitcoin volatility, as well as the volatility of any other digital asset, is in a different league. Although the reasons for price volatility in mainstream and cryptocurrency markets can be the same, including breaking news and market sentiment, the effect in the crypto market often leads to greater and faster price swings - both up and down.
The cryptocurrency market is relatively new and lacks a robust ecosystem of large trading firms and institutional investors, which results in less liquidity. It makes it vulnerable to trade movements of whale traders (those who own a large amount of cryptocurrencies). For example, news of a crypto influencer Elon Musk investing $1.5bn in bitcoin greatly contributed to bitcoin’s rally to its fresh all-time high of $64,800 on 14 April, 2021
Why is bitcoin so volatile? Another reason behind bitcoin’s volatility is its limited supply and lack of a central bank to control that supply. With 18.7 million bitcoins already in circulation, bitcoin’s supply is inelastic. It means a rise in demand can’t result in the rise of supply.
Other factors contributing to increased volatility in the cryptocurrency market include:
-
Negative: cyber attacks, for example, the hack of South Korea’s Bithumb exchange, which resulted in $30m in tokens stolen. Crypto restrictions, including the latest ban on providing cryptocurrency services in China.
-
Positive: adoption by big companies like Mastercard and Paypal, Tesla and Square.
Biggest BTC price swings
Cryptocurrency trading example
If you are wondering how to make money in cryptocurrency one way of getting started is to trade on the price of cryptocurrencies through contracts for difference (CFDs). Bear in mind you can also lose money trading CFDs. We’ve compiled a simple example and outlined the possible outcome.
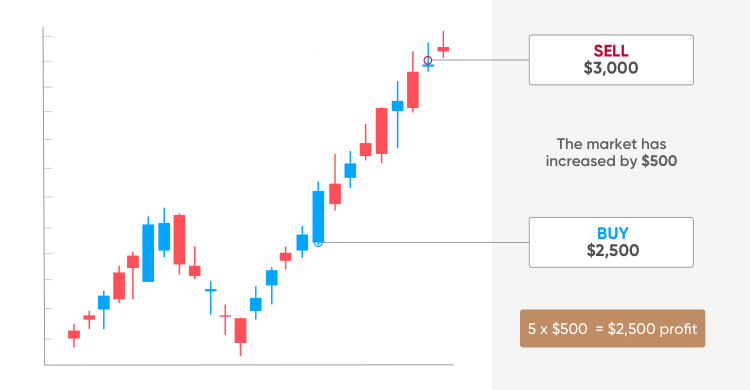
CFD trade: selling Ethereum (ETH)
The price of Ethereum’ coin, either (ETH), hit its all-time high of $4,362 on 12 May 2021 and fell to $1,900 by 23 May 2021. Let’s assume you believe the price of ether is going to rebound and decide to go long – buy ether against the US dollar (ETH/USD
In our example, the current market price of ether is $2,500 and you decide to buy five contracts (each equivalent to one ETH) to open a trade at this price (without leverage, i.e. 1:1).
Result A: a winning trade
If your prediction was right, and ether’s price moved up, your trade would be profitable. Let’s assume that the new ETH price is $3,008. You could close your position and take your profit by selling five contacts to close your position at the sell price of $3,000 (which is a bit lower than the mid-price due to the spread).
Because the market has moved $500 in your favour ($3,000-$2,500), the profit from your ETH trade would be: 5 x $500 = $2,500
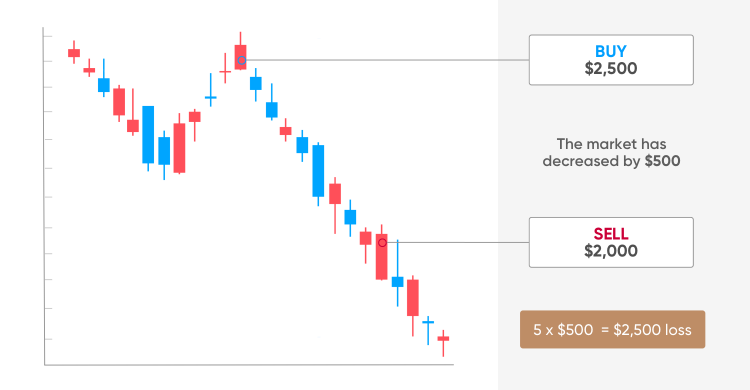
Result B: a losing trade
The cryptocurrency markets are extremely volatile and the market could go against you. If the price of ether fell, your position would be closed at a loss. Let’s assume you decide to exit the trade after the market fell to $2,008. So, you sell five contracts at the sell price of $2,000 (which is a bit lower than the mid-price due to the spread).
The market moved $500 against you ($2,500-$2,000), which means your loss will be: 5 x $500 = $2,500
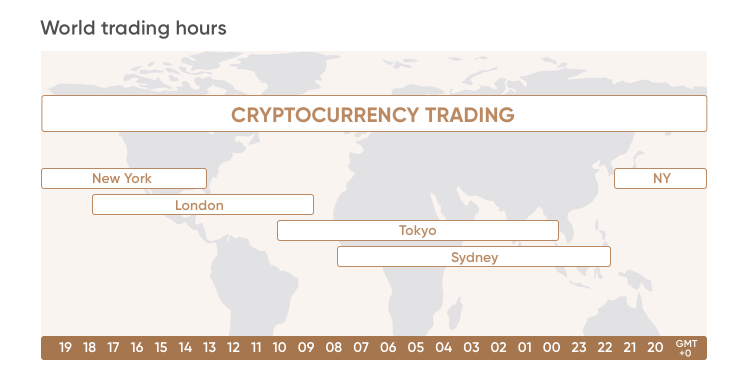
When can you trade cryptocurrency?
What hours of the day can you trade crypto? Cryptocurrencies are a product of the digital society, and just like the digital society, they run 24/7.
Can you trade crypto on weekends? You can trade cryptocurrencies at any point in the week. Unlike stocks and commodities, the cryptocurrency market isn’t traded on a regulated exchange. Instead, cryptocurrencies can be traded all hours of the day across an increasing number of crypto exchanges, such as Binance, Bitfinex or Coinbase Pro.
Although cryptocurrency trades around the clock, there are some periods that are more likely to be busier, however, this loose rule of thumb doesn’t always hold.
When are crypto markets busiest or most volatile?
Given that the USA, Russia and the UK are the three biggest crypto trading countries, it is unsurprising that the American through European crypto trading hours tend to be busier. The Asian market hours can be very volatile times for cryptocurrency, even on weekends.
It is not uncommon to see big moves occur in cryptocurrency prices over Sunday night (GMT); this can be damaging for people trading in European time zones. The peculiar thing about cryptocurrency exchanges is the extent to which the price can differ between each exchange.
For instance, there have been times where bitcoin has had up to a $500 price disparity across exchanges. The reasons for this disparity are related to the differences in liquidity across exchanges and often the geographical location of these exchanges. Price disparity becomes more noticeable just after big moves in the price of cryptocurrencies.
Is cryptocurrency a good investment?
A wild bitcoin run, Ethereum’s jump to its all-time highs and a surge of a meme-cryptocurrency dogecoin “to the moon” once again made people wonder if cryptocurrencies are good investments.
Is now a good time to invest in cryptocurrencies? It is not safe to say yes, because the cryptocurrency market is extremely volatile. We can’t say no, but a bullish momentum, turning into a crypto bloodbath and bounce back to new highs can bring trading opportunities.
Why is cryptocurrency a good investment? There are few reasons to consider:
Cryptocurrencies could be “the next big thing”.
Cryptocurrencies are going mainstream, attracting retail and institutional investors. People get interested in the fundamental value behind various cryptocurrency projects and their potential to change the financial services industry. Bitcoin is often referred to as “digital gold” and serves as a store of value. Bitcoin returns on investment have, for some, been high. For example, if you invested in one BTC when it cost $3,000, your profit would be $36,000 (at its current price of $39,000). However, if you invested in one BTC at its high of $64,800 you would have lost $25,800 (at BTC price of $39,000).
Cryptocurrencies can help to diversify your portfolio.
If you are ready to start trading crypto, a balanced portfolio might include a small portion of cryptocurrencies. Trading digital currencies have high potential for profit (or loss), if you make thorough decisions, use risk management tools, such as stop-loss and take-profit and trade with money you can afford to lose. If you are a long-term cryptocurrency investor, rather than a CFD trader, you can “hodl” (an acronym for “Hold on for dear life”) your coins, until it feels right to cash out
Please note that cryptocurrencies are volatile and hundreds of thousands of traders have seen losses as prices fall rapidly. You should do your own research, consider your attitude to risk and be prepared to lose money before deciding whether or not to invest.
How to buy cryptocurrency
There are two popular ways to get started buying cryptocurrency. One way is to buy cryptocurrency on exchanges, such as purchasing bitcoin on an exchange like Currency.com. Here you own the cryptocurrency yourself, wait for the price to rise significantly so you can sell it for a profit. Note that the market can go against you, the price might fall and you might make a loss.
You can also buy bitcoin in crypto ATMs, right from your Paypal account, or directly from other owners, using peer-to-peer tools like Bitquick and LocalBitcoins.com (stay cautious, buying from individuals).
Alternatively, you can trade a contract for difference (CFD) on a particular cryptocurrency.
How can I trade forex?
A CFD is a derivative product where a broker agrees to pay a trader the difference in the value of an underlying security between two dates; the opening and closing dates of the contract. How do I buy bitcoin with CFDs? You can either hold a long position (speculating that the price will rise) or a short position (speculating that the price will fall). For instance, when trading a Bitcoin CFD, you speculate on the BTC/USD price movement.
There are crucial differences between buying cryptocurrency and trading cryptocurrency CFDs. Due to overnight charges to maintain contract for difference positions, CFDs are not typically considered long-term investments
When purchasing cryptocurrency, you store it in a wallet, but when trading CFDs, the position is held in your trading account, which is regulated by a financial authority. You have greater flexibility when you trade with CFDs as you are not tied to the asset; you have merely bought or sold a derivative contract. You can also make money when the price falls - you take a short position (Sell). In this case, you will lose money if the price rises.
Note that CFD trading is risky. Contracts for difference are leveraged products, meaning your profits can be magnified, but if the market goes against your position, your losses are bigger too.
Cryptocurrency trading strategy
There are numerous trading strategies you can choose from to build your own effective trading framework. The best traders have a strategy based on research, which may include setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, restricting the size of trades and having a balance of assets, like traders do with stocks, commodities, indices, and forex. Speculating on the cryptocurrency markets with a solid trading strategy may help you to limit your risk.
For example, you can choose from the list of most popular trading strategies, build your own trading plan and adjust it according to your personal needs.
Day trading cryptocurrency strategy.
One of the most popular active trading strategies, day trading, involves frequent portfolio management and constant position monitoring. Day trading presupposes entering and exiting positions during one day with the major goal to capitalise on intraday price movements of an asset.
When it comes to cryptocurrency markets, which are open 24 hours a day 365 days a year, the meaning of day trading slightly differs. Usually it refers to a short-term trading approach, when traders open and close their positions within 24 hours or less.
Swing trading cryptocurrency strategy
Swing trading is a longer-term trading strategy. Traders usually hold positions for longer than one day, but usually no longer than a month. Swing traders usually try to benefit from volatility waves, which often last for several days or weeks. They use a combination of fundamental and technical analysis to make thorough trading decisions. Swing trading enables you to make more rational decisions with less rush.
Trend trading
Also referred to as position trading, trend trading strategy suggests traders hold positions for a longer timeframe, usually for a couple of months. Trend traders try to benefit from the cryptocurrency’s directional trends. Usually, they open a long position in an uptrend and go short in a downtrend. They mostly rely on fundamental factors behind the asset’s price action, considering events that might take a longer time to play out. However, trend traders should always consider the possibility of a trend reversal.
Scalping
One of the fastest trading strategies, scalping does not wait for big moves or clear trends to play out. Scalpers specialise in using small price movements again and again. They do not keep their trades open for long. Instead, they can open and close positions in a matter of seconds. Scalping is considered an advanced trading strategy, which is not recommended for beginners. It is often used by whale traders (those holding large amounts of that crypto). As the percentage profit targets are small, larger positions make more sense.
Advantages of using CFDs for cryptocurrency trading

Liquidity. Liquidity measures how easily an asset can be turned into cash, without impacting the market price. If an asset is more liquid, it brings about better pricing and faster transaction times. The cryptocurrency market is considered illiquid, partly due to the distribution of orders across exchanges, as noted by price disparity. This means that a relatively small number of trades can have a large impact on market prices; one factor contributing to cryptocurrency volatility. However, when trading CFDs on cryptocurrencies, you can gain exposure a lot easier because you are not trying to buy the underlying asset, simply a derivative product.
Leverage. CFDs can be traded on margin. This means a trader only needs to put down a fraction of the value of their trade, and in essence, borrow the remaining capital from their broker. This allows for more accessibility, greater exposure and amplified results. This can be particularly useful for cryptocurrencies, given the huge volatility the asset class witnesses, but this also brings increased risks.
Ability to go long or short. When purchasing cryptocurrency itself, you can only profit when the market is rising. However, with equitypinnacle.com, you can profit in both falling and rising markets due to the ability to short sell CFDs on cryptocurrency. If the trade goes against you can make losses too.
Tax-efficient trading: Trading CFDs on a cryptocurrency can offer benefits over holding the cryptocurrency itself. CFDs are useful for hedging your existing portfolio because if your expectations are wrong, in certain jurisdictions, you can offset any losses incurred with CFDs against the capital gains charged on the increase of your portfolio.
Note: CFDs are considered a short-term investment due to overnight charges for maintaining positions.
Still looking for a broker you can trust?
Join the 50.000+ investors that chose to trade with equitypinnacle.com
1. Create & verify your account
2. Make your first deposit
3. You’re all set. Start trading
Also you can contact us: support@equitypinnacle.com
Markets
Products
- products
Learn to trade
- Popular markets guides
- Trading guides
About
- Partner with us
Risk warning: transactions with non-deliverable over-the-counter instruments are a risky activity and can bring not only profit but also losses. The size of the potential loss is limited to the funds held by us for and on your behalf, in relation to your trading account. Past profits do not guarantee future profits. Use the training services of our company to understand the risks before you start operations.
Closed joint-stock company “Equity Pinnaclets” is regulated by NBRB, registered 19.03.2018 with company registration number 193222154. Certificate of inclusion in the register of forex companies No. 16 dated 16.04.2018.
