What is CFD trading and how does it work?
Contracts for difference (CFD) are a popular way of trading on the price of stocks and indices, commodities, forex and cryptocurrencies without owning the underlying assets. Learn everything you should know about CFD trading and how to use CFDs to go long and short on assets.
Get started- Learn to trade
- Trading guide
- CFD trading guide
- What is CFD trading and how does it work?
What is a contract for difference (CFD)?
A contract for difference (CFD) is a popular type of derivative in finance. Derivatives are time-limited contracts that ‘derive’ their value from the market performance of an asset. This guide has everything you need to know about CFD trading explained in simple terms.
So what does CFD mean in trading? CFDs allow you to speculate on various financial markets, including stocks, indices, commodities, forex pairs, and cryptocurrencies. You never buy the assets, but trade on the rise or fall in their price, usually over a short period of time.
A CFD is a contract between a broker and a trader who agree to exchange the difference in value of an underlying security between the beginning and the end of the contract, often less than one day.
A contract for difference (CFD) is:
-
A derivative - you do not own the underlying asset
-
An agreement between you and your broker
-
Based on the change in price of the asset
-
Over a short time period
What are CFDs?
A contract for difference (CFD) lets you trade with just a fraction of the value of your trade, which is known as trading on margin, or leveraged trading. This allows traders to open larger positions given their initial capital. Therefore, CFD trading offers greater exposure to global financial markets.
One of the major benefits of CFD trading is that you can speculate on the asset’s price movements in either direction. You simply buy or sell a contract depending on whether you believe the asset’s price will go up or down. You open a long or a short trade accordingly.
However, you should always note that leverage trading can amplify your wins, but can also boost your losses.
How does CFD trading work?
When you open a contracts for difference (CFD) position you select the number of contracts (the trade size) you would like to buy or sell. Your profit will rise in line with each point the market moves in your favour.
Buy
If you think the price of an asset will rise, then you would open a long (Buy) position and profit if the asset price rises in line with your expectations.
Sell
If you think the price of an asset will fall then you would open a short (Sell) position and profit if it falls in line with your prediction.
What is a CFD account?
A contract for difference (CFD) account enables you to trade on the price difference of various underlying assets using leverage. Leverage means you put up only a fraction of the amount needed to trade. This is called deposit margin. You will also need to have enough in your account to cover any potential losses if trades go against you. This is called maintenance margin.
Your broker needs to know a little about you before they can offer you margin trading, so they ask you to set up a special account, proving your identity and ability to cover losses. Often you can practise trading in a demo account, but you will need to add funds to create a CFD trading account before you can trade properly.
Some regulators require that new customers pass an ‘appropriateness’ test. This often means answering some questions to demonstrate that you understand the increased risks – and not just the potential rewards – of trading on margin. It’s best to thoroughly educate yourself on how leverage and margin work before trading.
What is leverage in CFD trading?
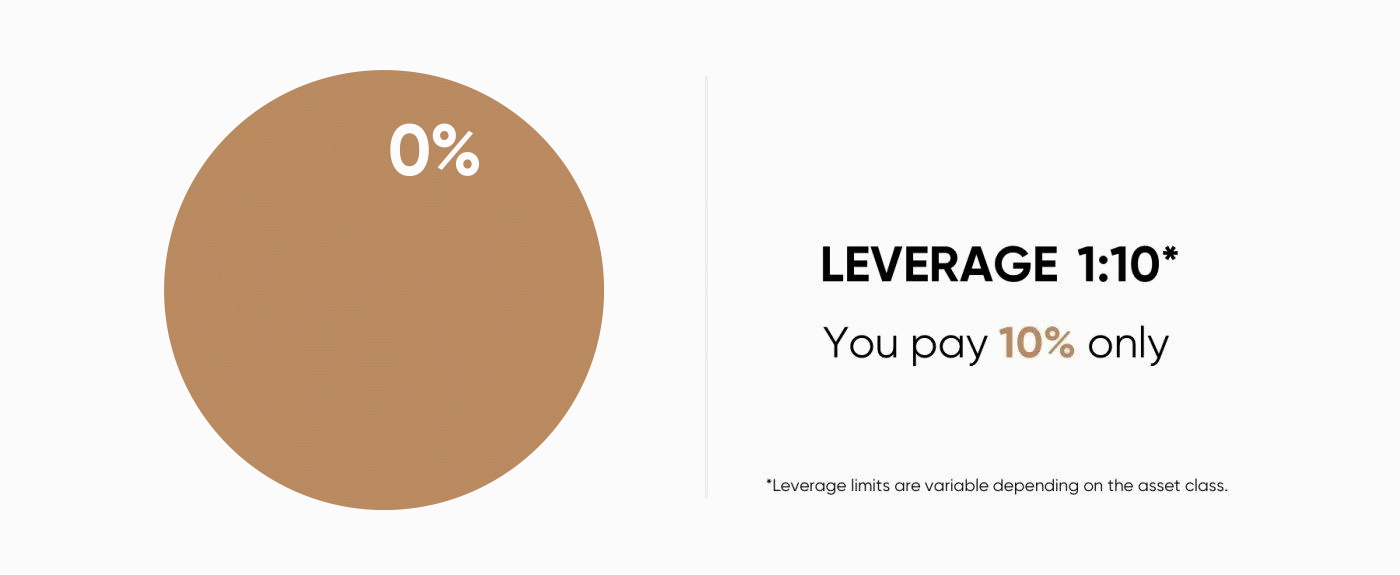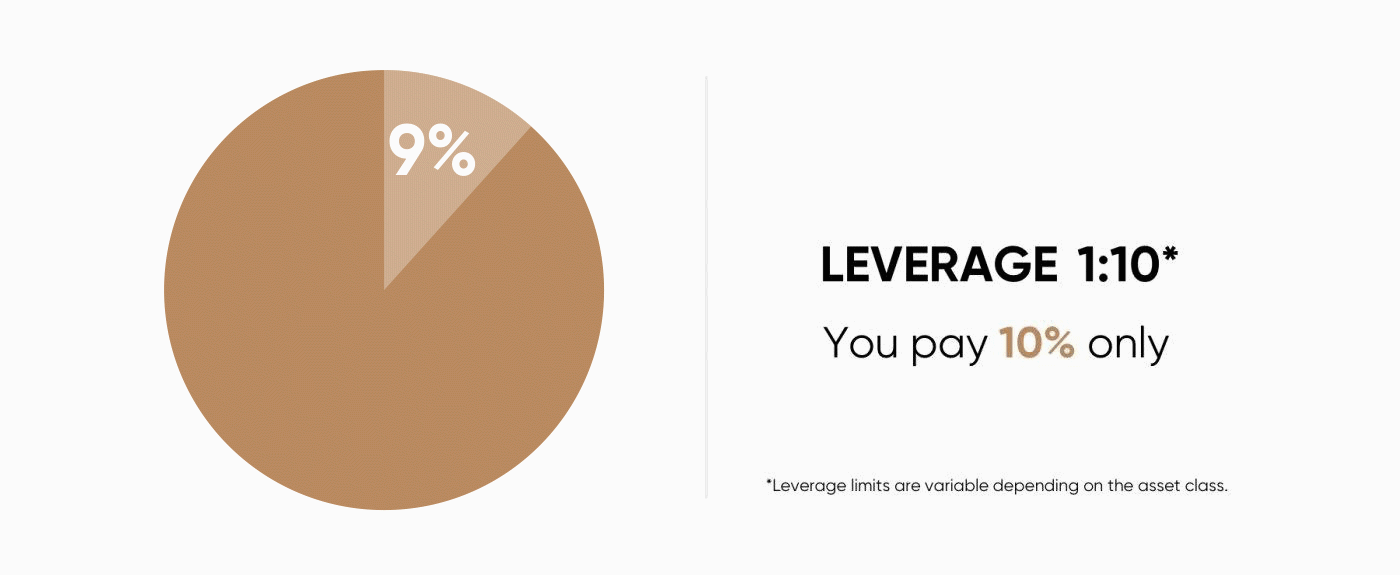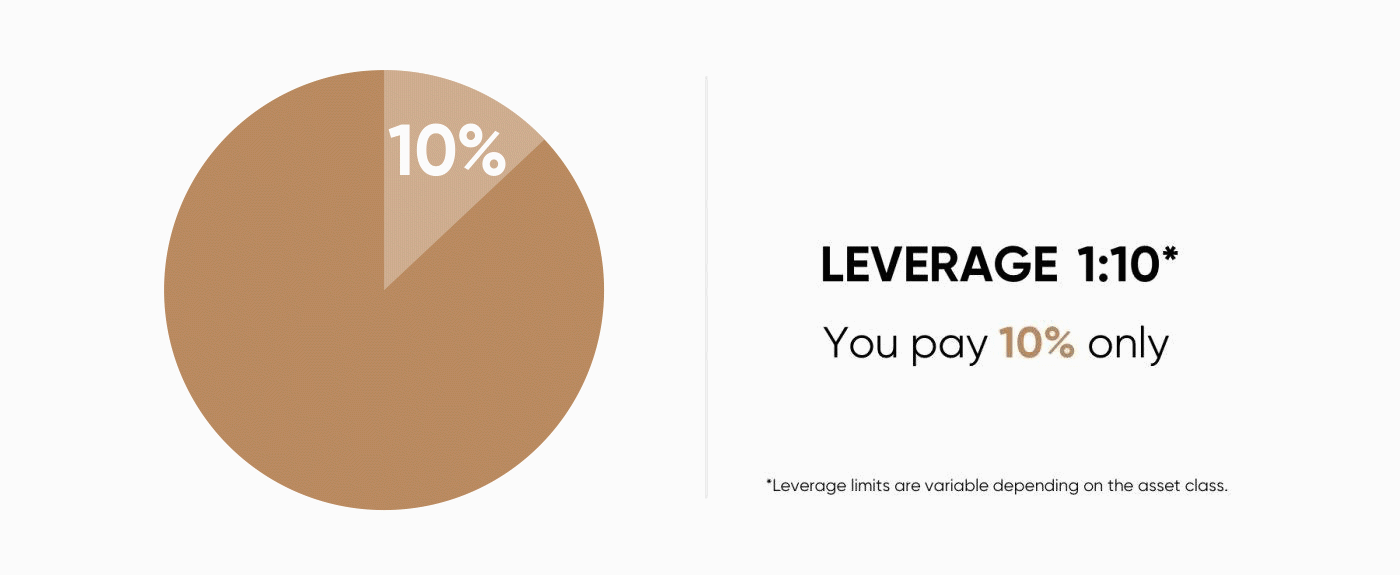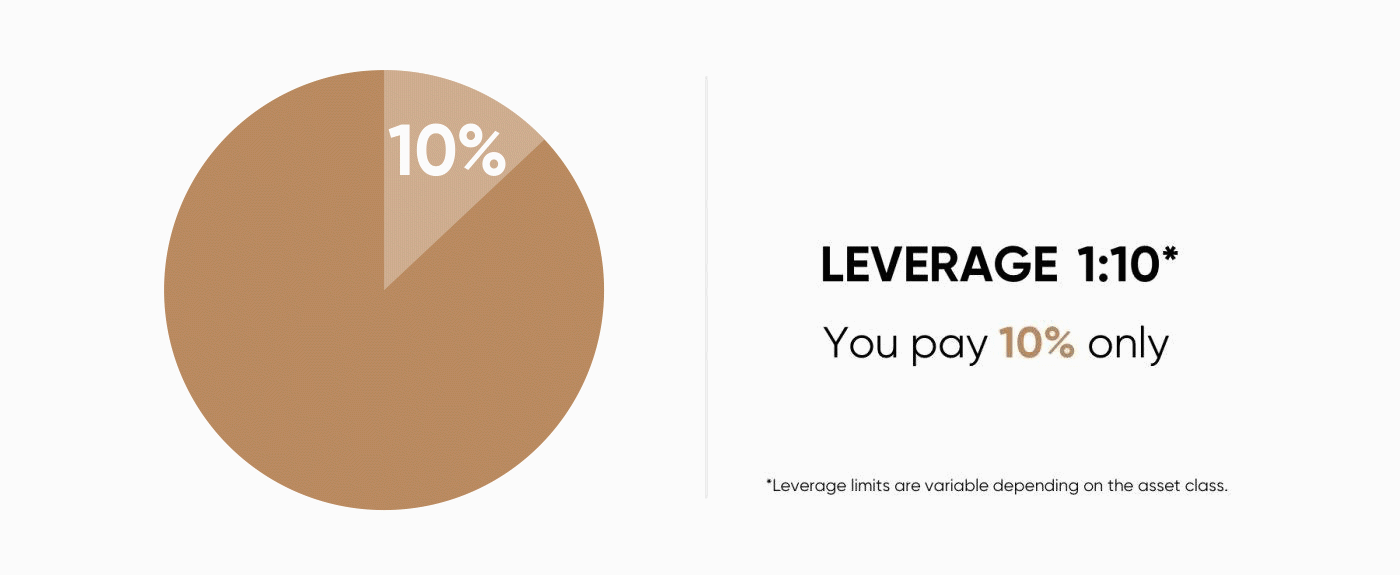
When you are trading contracts for difference (CFDs), you hold a leveraged position. This means you only put down a part of the value of your trade and borrow the remainder from your broker.Leveraged trading is also referred to as trading on margin. A10% margin means that you have to deposit only 10% of the value of the trade you want to open. The rest is covered by your CFD provider.
For example, if you want to place an order for $1,000 worth of Brent crude oil and your broker requires 10% of margin, you will need only $100 as the initial amount to open the trade.
Spread and commission
With CFD trading, you’re always offered two prices based on the value of the underlying instrument: the buy price (offer) and the sell price (bid).
The price to buy will always be higher than the current underlying value and the sell price will always be lower. The difference between these prices is called the CFD spread. At Capital.com, we do not charge CFD commission on any trades made with us.
-
The Buy price (offer) is the price at which you start, or open, a long position
-
You close your position when you Sell
-
The Sell price (bid) is the price at which you open a short position
-
You close your position when you Buy

For example, if you expect the price of gold to increase you may want to open a position with a CFD on gold. Imagine the quoted price is $1,200/$1,205 (this is the bid/ask spread) and you buy 100 CFDs on gold (taking a long position). The size of the position taken (the contract value) is illustrated below.
How much should you invest?
CFD trading democratises the markets by providing a low entry level. Capital.com has traders who open positions worth more than $1m a time but the minimum deposit you can trade with is just $20 (€20, £20, 100PLN).
f you are using wire transfer the minimum deposit is €250.
You can open an account for free and practise in demo mode. Capital.com is a flexible and scalable solution for everyone, regardless of your risk appetite, experience or the amount of money you have to trade.
CFD trading is considered a cost-effective way of entering the financial markets. With some brokers, CFD costs include a commission for trading various financial assets, however, Capital.com doesn’t take commissions for opening and closing trades, for deposits or withdrawals.
The major CFD cost is the spread – the difference between the buy and sell price at the time you trade. There is an additional charge of an overnight fee, which is taken if a trade is kept open overnight.
As contracts for difference are leveraged products, you can open much larger positions with a lower initial deposit than you need to buy traditional shares. For example:
Still looking for a broker you can trust?
Join the 50.000+ investors that chose to trade with equitypinnacle.com
1. Create & verify your account
2. Make your first deposit
3. You’re all set. Start trading
Also you can contact us: support@equitypinnacle.com
Markets
Products
- products
Learn to trade
- Popular markets guides
- Trading guides
About
- Partner with us
Risk warning: transactions with non-deliverable over-the-counter instruments are a risky activity and can bring not only profit but also losses. The size of the potential loss is limited to the funds held by us for and on your behalf, in relation to your trading account. Past profits do not guarantee future profits. Use the training services of our company to understand the risks before you start operations.
Closed joint-stock company “Equity Pinnaclets” is regulated by NBRB, registered 19.03.2018 with company registration number 193222154. Certificate of inclusion in the register of forex companies No. 16 dated 16.04.2018.
